nivek
As Above So Below
July 2023: Extreme Weather, Planetary Upheaval, Meteor Fireballs.
View: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=blWYoXyVdBA
.
View: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=blWYoXyVdBA
.
This white paper summarizes the views of the CO 2 Coalition, a new and
independent, non-profit organization that seeks to engage thought leaders, policy
makers, and the public in an informed, dispassionate discussion of how our planet
will be affected by CO 2 released from the combustion of fossil fuel. Available
scientific facts have persuaded Coalition members that additional CO 2 will be a net
benefit. Rather than immediately setting this document aside for promoting such
a politically incorrect view, readers would do well to act on the ancient motto of
Britain’s prestigious Royal Society—nullius in verba, “don’t take anyone’s word for
it,” or more simply, “see for yourself.”
Claims that “97 percent of scientists” agree that a climate catastrophe is looming
because of the emission of CO 2 should be greeted with skepticism. Traditional
science has advanced by comparing observations or experiments with theoretical
predictions. If there is agreement with theory, confidence in the theory is increased.
If there is disagreement, the theory is abandoned or it is modified and tested again
against observations.
Scientific truth has never been established by consensus, for example, by “97
percent agreement.” History reveals many instances when the scientific consensus
of the day was later discredited. The widespread embrace and practice of eugenics
in the early 1900s; opposition to the theory of plate tectonics in geology; and the
dominance of Lysenkoist biology in the Soviet bloc, are a few recent examples. Given
the frequency of mistaken consensus, citizens everywhere should heed the Royal
Society’s motto and learn as much as they can about how increasing CO 2 levels in the
atmosphere will affect the planet.
Interesting about HAARP.Scientists have said the earth goes through temperature changes all by it own. but "this is just my belief" all that plastic out in the ocean that made a literal garbage island. Could disrupt the natural flow of the sea currents which in turn would make winds change. Pumping oil deposits dry which where between us and Magma, would make things hotter. Not to mention those idiots and HAARP super heating our ionosphere with Basically a Giant Microwave Death Laser... I mean Humans as a species do get up to some Grade A Fuckatry... I do not believe Cow farts and burps are really the cause of anything except humans wanting a reason to stay stocked up on Double Quarter pounders with cheese.
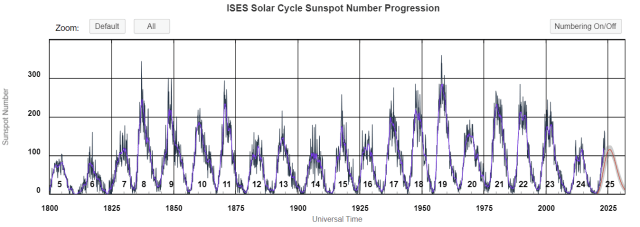
From 1650 to 1710, temperatures across much of the Northern Hemisphere plunged when the Sun entered a quiet phase now called the Maunder Minimum. During this period, very few sunspots appeared on the surface of the Sun, and the overall brightness of the Sun decreased slightly. Already in the midst of a colder-than-average period called the Little Ice Age, Europe and North America went into a deep freeze: alpine glaciers extended over valley farmland; sea ice crept south from the Arctic; and the famous canals in the Netherlands froze regularly—an event that is rare today.
 suk
suk

